On 9 April the European Court docket of Human Rights (ECtHR) issued its first ever complete resolution in a local weather litigation case. The judges of the Court docket’s Grand Chamber discovered that Switzerland was in breach of its optimistic obligations to guard the well being, well-being and high quality of lifetime of Swiss residents from the impacts of local weather change. This violation was attributed to the Swiss authorities’s failure to implement the sturdy regulatory framework needed for fulfilling its dedication to cut back emissions as set out within the Paris Settlement.
Because the mud begins to decide on this case, the vital query within the minds of many is what implication the judgment can have for a way Switzerland and the 45 different signatories of the European Conference on Human Rights (ECHR) now deal with local weather change.
Might this ruling catalyse the fast cross-cutting motion that’s urgently wanted to fight local weather change?
Firstly, this can be a query of compliance: will Switzerland and the opposite ECHR signatories discover the judgment a compelling cause to amend their local weather legal guidelines according to the steering given by the court docket? Most commentators have centered on this component. Whereas there seems to be a common consensus that the ruling can be “transformative”, some have handled it extra cautiously. Specifically, whereas the case is anticipated to have “knock-on” results on legislation and policymaking on the home and worldwide ranges, the extent of those impacts will take time to crystallise. Some researchers argue that, with its ruling, the ECtHR has merely set a “minimal normal” and thus they query whether or not it is going to result in ECHR signatories considerably tightening their local weather legal guidelines.
However importantly, that is additionally about effectiveness: can the kind of regulatory framework envisioned by the ECtHR drive international locations to satisfy their legislative local weather commitments? We focus our evaluation beneath on this side, in search of to evaluate how efficient the kind of regulatory framework envisioned by the Court docket could be in accelerating credible local weather motion.
A home regulatory framework aligned with human rights obligations
In its judgment, the ECtHR set out a collection of minimal necessities {that a} home local weather change regulatory framework should meet to align with human rights obligations. These are firmly grounded within the structure of the Paris Settlement, reflecting world practices in local weather governance and powerful scientific foundations.
Local weather framework legal guidelines have emerged as a distinguished software to drive home local weather motion, together with establishing regulatory frameworks. Thus far, 59 international locations, together with 25 ECHR signatories, have enacted local weather framework legal guidelines. These legal guidelines set the strategic course for nationwide local weather insurance policies, and likewise typically embrace long-term local weather goals: for instance, 17 international locations’ legal guidelines comprise internet zero or local weather neutrality targets.
The scope of local weather framework legal guidelines varies considerably, nonetheless. Some international locations, like Nigeria, arrange inter-ministerial coordination our bodies to arrange nationwide local weather motion plans designed to satisfy targets, whereas others like Canada mandate interim targets or carbon budgets primarily based on the recommendation of impartial skilled advisory our bodies. In some circumstances, like Japan, laws individually addresses mitigation and adaptation efforts. At occasions, international locations additionally set up home governance processes throughout a number of legal guidelines, government insurance policies or by way of casual processes.
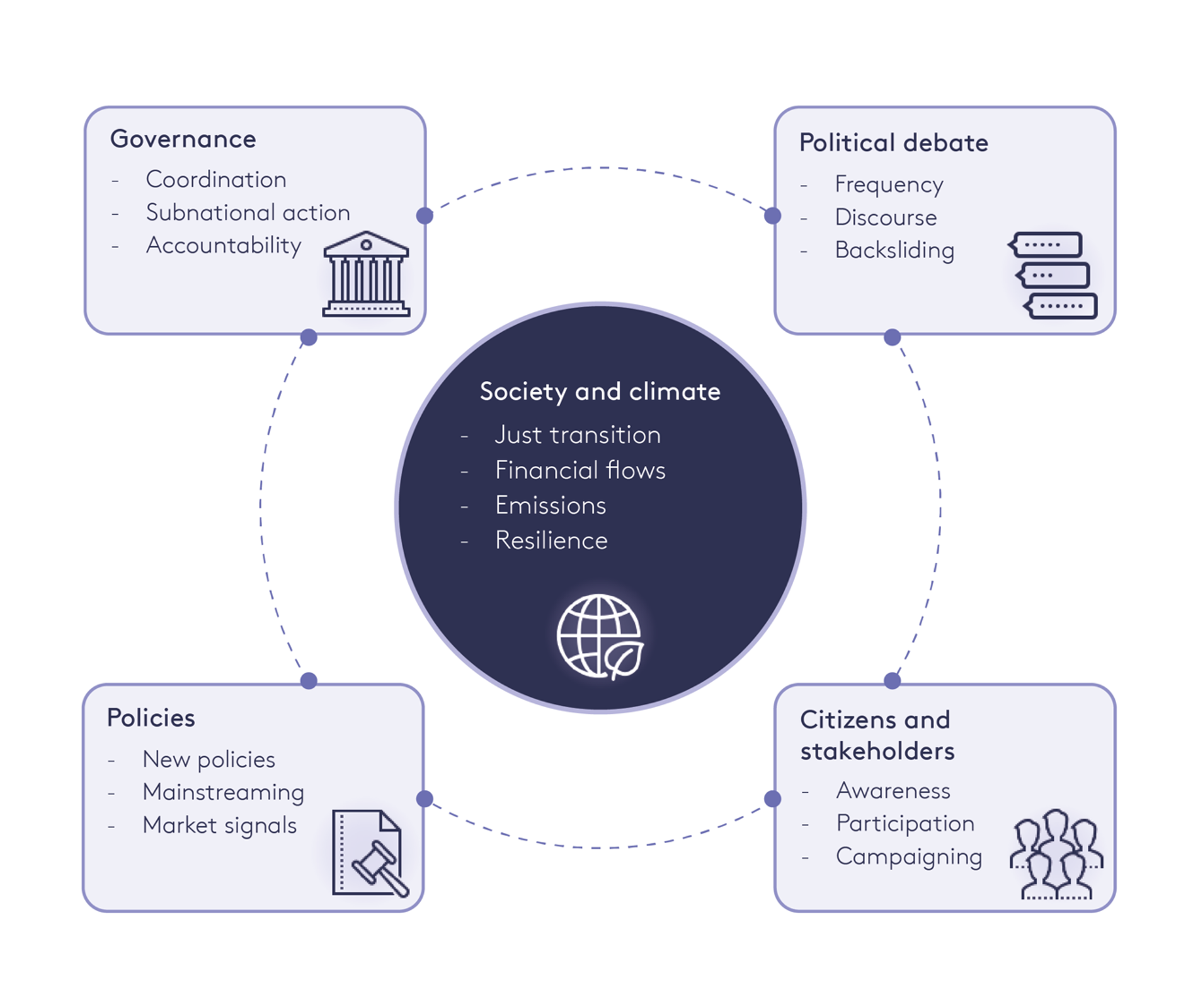
Sadly, in the case of understanding the affect of such local weather framework legal guidelines, empirical proof stays restricted, notably concerning how impacts would possibly differ throughout totally different socioeconomic and political contexts. Nonetheless, analysis carried out by the Grantham Analysis Institute into the impacts of local weather framework legal guidelines within the UK, and most not too long ago in Germany, Eire and New Zealand, has uncovered diverse impacts throughout 5 key areas (see Determine 1). These findings point out that essentially the most vital impacts of local weather framework legal guidelines are noticed within the areas of governance and political debate.
Determine 1. Impacts of local weather framework legal guidelines
Supply: Averchenkova et al. (2024)
Mapping the Court docket’s minimal necessities in opposition to the constructing blocks of efficient local weather legal guidelines
The ECtHR’s specified set of minimal necessities for a State’s regulatory framework on local weather change (paragraph 550 of the judgment) align carefully with what our analysis identifies because the core constructing blocks of efficient local weather framework legal guidelines – see Desk 1 beneath. Not solely do these parts of local weather legal guidelines have essentially the most direct affect, in addition they result in essentially the most vital impacts. Our analysis reveals that these constructing blocks immediately contribute to the robustness of regulatory frameworks, making certain that local weather motion is each bold and grounded in scientific proof.
Desk 1. The ECtHR’s minimal necessities mapped in opposition to our recognized constructing blocks for efficient local weather framework legal guidelines
The similarities between the ECtHR’s stipulated necessities for local weather regulatory frameworks and the constructing blocks that make local weather framework legal guidelines only recommend that the method required by the Court docket might have vital optimistic impacts.
Nonetheless, whereas the recognized elements are essential, they will not be adequate on their very own to catalyse fast and enduring change. For instance, though many local weather framework legal guidelines mandate public session, the specifics of those processes are sometimes imprecisely outlined, leaving uncertainty about how public participation, stakeholder engagement and deliberative processes are to be constantly or formally built-in into an institutional framework. This integration is important for making certain public acceptance of local weather insurance policies.
The ECtHR addressed this want in paragraph 554 of its judgment, underscoring the significance of public participation and entry to info in creating local weather insurance policies. The extent to which this side of the judgment will affect future legislative practices and enhance the inclusivity and effectiveness of local weather governance stays an open query.
Useful steering from the Court docket – however in the end it comes right down to political will
Our analysis additionally highlights that there are vital challenges to implementing local weather framework legal guidelines: particularly, with out sustained political will, enforcement turns into very tough. One other recurring challenge is the absence of stringent penalties for non-compliance, which undermines the credibility of those legal guidelines and poses dangers to democratic accountability. Litigation, whereas a final resort, can strengthen each administrative and political accountability for fulfilling local weather commitments. The KlimaSeniorinnen ruling highlighted vital gaps in Switzerland’s regulatory framework and its failure to satisfy earlier emissions targets, underscoring the judiciary’s function in holding states accountable for his or her local weather obligations.
The ECtHR has set out clear instructions for member states to observe to align their local weather insurance policies with human rights obligations. Home legislators throughout Europe should give these necessities critical consideration to make sure their local weather legal guidelines not solely meet these minimal requirements but in addition successfully contribute to world local weather objectives. That is crucial for each environmental sustainability and the safety of elementary human rights that local weather change is affecting.